
Welcome to visit: Beijing Trinova Auto Tech Co.,Ltd
High level autonomous driving core component: Trinova wire controlled steering solution
- Categories:News center
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2023-09-08 10:00
- Views:
(Summary description)The automotive industry is rapidly developing under the guidance of the "new four modernizations" goals, and significant achievements have been made in the electrification and intelligence of automobiles.
High level autonomous driving core component: Trinova wire controlled steering solution
(Summary description)The automotive industry is rapidly developing under the guidance of the "new four modernizations" goals, and significant achievements have been made in the electrification and intelligence of automobiles.
- Categories:News center
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2023-09-08 10:00
- Views:
Introduction:
The automotive industry is rapidly developing under the guidance of the "new four modernizations" goals, and significant achievements have been made in the electrification and intelligence of automobiles. The development of automotive intelligence has put forward new demands for automotive chassis. Traditional automotive chassis can no longer meet the requirements of intelligent vehicles in terms of response speed, execution accuracy, safety, etc. The automotive chassis is transitioning from traditional chassis to wire controlled chassis. Among them, Steering-by Wire (SBW) is the core component in the steering-by wire chassis that controls lateral motion and is an important actuator for achieving high-order autonomous driving. The "Development Plan for the New Energy Vehicle Industry (2021-2035)" issued by the State Council lists the integration of pure electric vehicle chassis and wire control execution system as key technical research projects. The national standard "GB17675-2021 Basic Requirements for Automotive Steering Systems" has removed the requirement that full power steering mechanisms should not be installed (3.3 in 1999), and regulations have allowed for physical decoupling between the steering wheel and the steering gear of the steering system. The promotion of national strategy and the implementation of regulatory standards have a direct promoting effect on the large-scale industrial application of SBW products. This article will provide a detailed introduction to Trinova Huizhi's SBW solution from the development path, technical solutions, key technologies, and other aspects of steering technology.
1、 Turning to the path of technological development
The steering system is one of the key components of the automotive chassis, playing a crucial role in the stability, safety, and comfort of the vehicle. With the deepening of electrification in the automotive industry, the steering system has gone through a development process from mechanical steering system (MS), mechanical hydraulic power steering system (HPS) to electronic hydraulic power steering system (EHPS), electric power steering system (EPS), and then to control by wire steering (SBW).
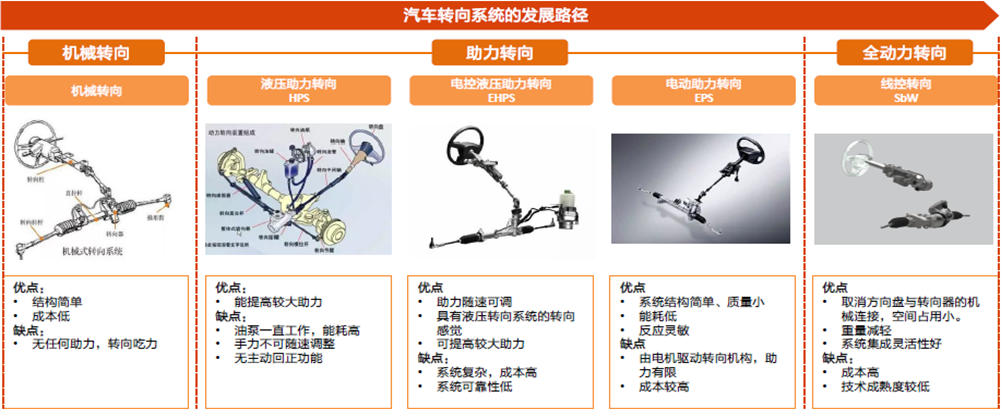
Figure 1-1 Development Path of Automotive Steering System
Compared to mechanical and hydraulic steering systems, electric power assisted steering (EPS) has a simpler structure, faster power control response, lower energy consumption, and does not require maintenance and upkeep. It is currently the mainstream product of automotive steering systems. The biggest difference between SBW and EPS is that there is no mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the actuator, so it has obvious advantages in cost control, design flexibility, functional richness, spatial layout, and other aspects.The steering system, as a core component of the chassis, has a high technical barrier. China's automotive industry started relatively late, so currently, supplier giants from Germany, the United States, Japan, and South Korea still dominate the majority of the steering system market, especially high-end EPS and Steer By Wire (SBW) systems, which are still in a catching up state in China. However, with the gradual maturity of the domestic automotive industry chain, some enterprises are also gradually mastering the core technology of steering systems, and are expected to rapidly increase their market share in the future.
2、 Trinova Wire Control Steering Technology Solution (T-SBW)
2.1Trinova wei Intelligent T-SBW System Solution
As shown in Figure 2-1, the schematic diagram of Trinova Huizhi's SBW system scheme is mainly composed of steering wheel actuator (HWA) and front wheel actuator (RWA). The biggest difference between SBW and EPS systems is that there is no intermediate shaft, which means that the steering wheel actuator is mechanically completely decoupled from the front wheel actuator. Therefore, it has a more flexible and adjustable steering ratio and more comfortable road feedback. At the same time, it also provides the possibility of steering wheel silence and folding in autonomous driving scenarios.
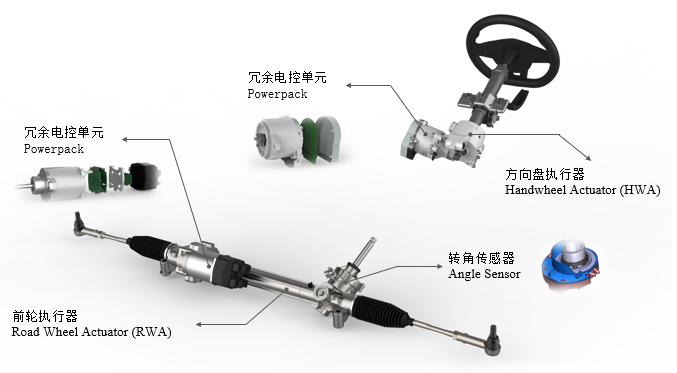
Figure 2-1 Schematic diagram of Trinova Intelligent T-SBW system solution
Handwheel actuator (HWA): mainly composed of steering wheel, steering column, reducer, TAS sensor, and redundant electronic control unit, its main function is to obtain the driver's intention and provide the desired steering wheel angle signal to the front wheel actuator (RWA). At the same time, it simulates the road feedback force of the vehicle based on the rack force feedback from the front wheel actuator, providing the driver with road feel feedback information.
Road Wheel Actor (RWA): The front wheel actuator consists of a mechanical steering gear, angle sensor, redundant electronic control unit, etc. Its main function is to receive the expected angle command sent by the steering wheel actuator (HWA), and control the motor to achieve lateral movement of the rack, ultimately achieving steering function.
● Redundant electronic control unit (Fail Operational Powerpack): Both the steering wheel actuator (HWA) and front wheel actuator (RWA) require an electronic control unit as the actuator to achieve road feel feedback control and front wheel steering functions, respectively. The use of redundant electronic control units is mainly to support high-order autonomous driving conditions, that is, in autonomous driving scenarios, if any single point of failure occurs in the steering wheel actuator (HWA) or front wheel actuator (RWA) of the SBW system, the component must have a fail operational function to ensure that the road feel is not lost or the front wheels do not lose steering ability. The steering wheel actuator (HWA) and front wheel actuator (RWA) electronic control units of the Trinova Steer By Wire (SBW) system both adopt a fully redundant electronic control scheme to drive a six phase permanent magnet synchronous motor. After a single point failure, the system still has the ability to provide road feel feedback and execute steering control.
Angle Sensor: The front wheel actuator (RWA) needs to accurately track the desired angle, so an angle sensor is required to measure the actual input angle of the pinion.
2.2 Trinova Intelligent T-SBW Electrical Architecture
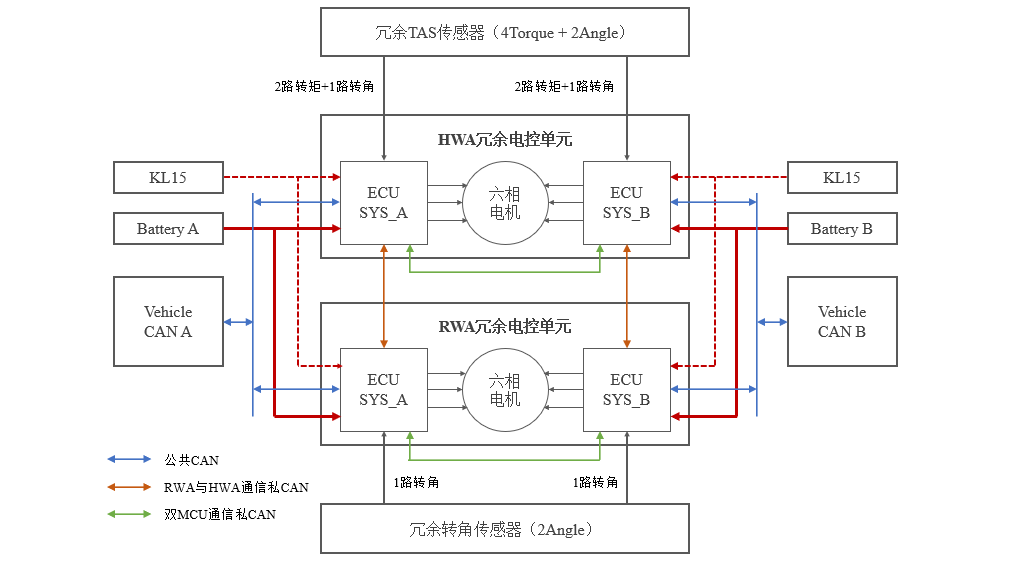
Figure 2-2 Electrical Architecture Diagram of Trinova Intelligent T-SBW
As shown in Figure 2-2, the electrical architecture diagram of the Trinova Steer by Wire (SBW) system is shown. The vehicle has redundant power supplies and a common CAN communication network. The steering wheel actuator (HWA) and front wheel actuator (RWA) both use fully redundant electronic control units, which are connected to different power supplies and CAN communication networks to achieve independent electrical isolation outside the two systems. The fully redundant electronic control unit also achieves signal interaction between the two ECUs through CAN communication, allowing for signal interaction and collaborative control. The steering wheel actuator (HWA) and front wheel actuator (RWA) communicate through private CAN, transmitting desired angle signals, rack force signals, etc. Each ECU of the steering wheel actuator (HWA) needs to collect dual torque signals and single absolute angle signals (supporting functional safety ASIL D level), thus corresponding to the "4+2" TAS sensor; Each front wheel actuator (RWA) ECU needs to collect a single absolute angle signal (supporting functional safety ASIL D level), so it corresponds to an angle sensor with two angle signals.
2.3 Trinova wei Intelligent T-SBW Algorithm Architecture
Figure 2-3 shows the schematic diagram of the algorithm architecture of the Trinova Steer By Wire (SBW) system. According to the functions of the steering wheel actuator (HWA), the main algorithms implemented include reference hand force calculation, torque superposition control, hand force tracking control, angle superposition control, variable transmission ratio control, angle command calculation, etc. It can be seen that in the steering by wire (SBW) system, the steering wheel actuator (HWA) relies on the torque closed-loop algorithm to achieve the driver's tactile control, which is completely different from the traditional EPS open-loop torque algorithm. The main algorithms of the front wheel actuator (RWA) include angle tracking control and rack force estimation algorithms. Corner tracking control measures the angle of the small gear through a corner sensor as a feedback signal, achieving closed-loop control of the angle and achieving precise steering control. The rack force estimation algorithm observes the rack force of the steering gear and sends it as a road feel feedback signal to the steering wheel actuator (HWA) to achieve road feel feedback simulation calculation.
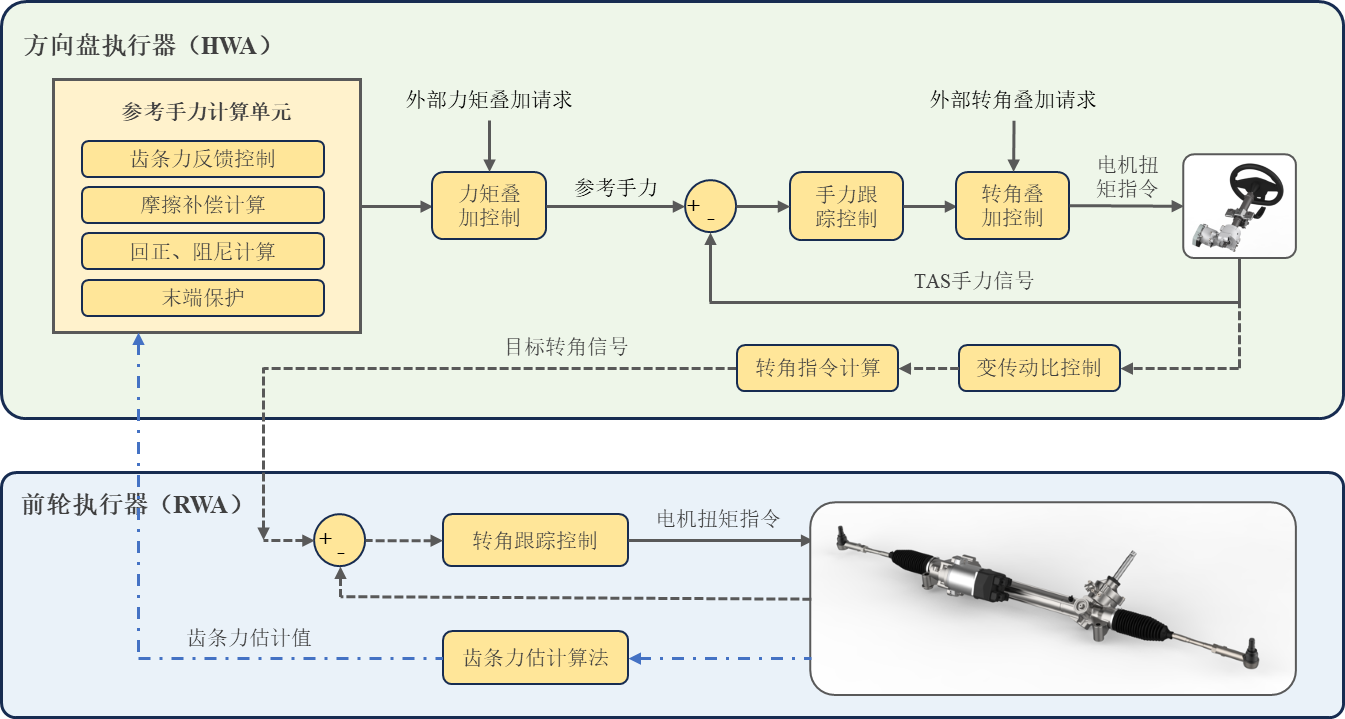
Figure 2-3 Schematic diagram of the algorithm architecture of Trinova Intelligent T-SBW system
3、 Key Technologies ofTrinova Intelligent T-SBW
3.1 Observation of rack force
As shown in Figure 3-1, the rack force estimation algorithm architecture of the front wheel actuator (RWA) for steering by wire is presented, which uses the vehicle model based rack force estimation method (Vehicle Estimator) and the steering system model based estimation method, respectively
Tianjin Trinova Auto Tech Co.,Ltd
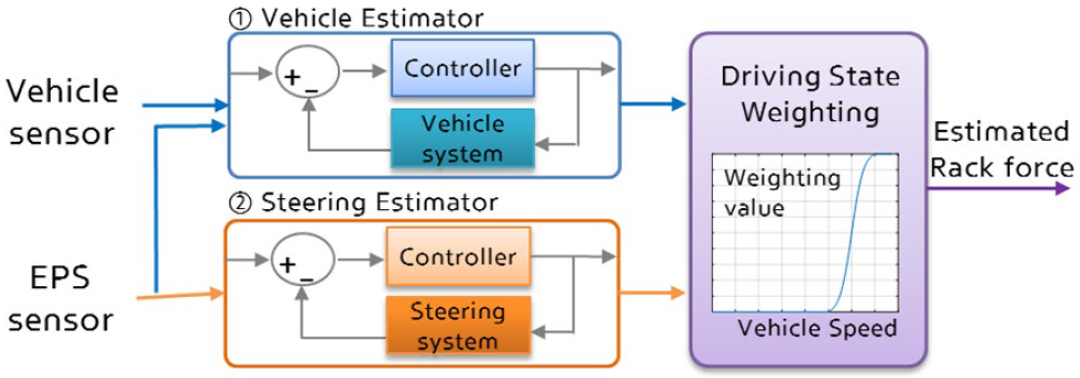
Figure 3-1 Schematic diagram of rack force estimation algorithm
Image source: Kim, C, Son, D, Sabato, Z, And Lee, B, Improvement of Steel Performance Using Steel Rack Force Control, SAE Technical Paper 2019-01-12342019, https://doi.org/10.4271/2019-01-1234.
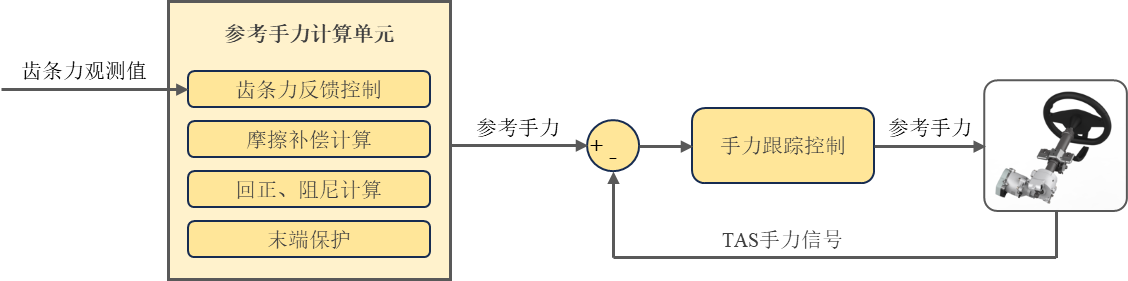
Figure 3-2 Schematic diagram of HWA torque closed-loop algorithm
3.3 Advanced functions of wire controlled steering
● Customization of driving feel:
Compared to traditional EPS, Steer By Wire (SBW) eliminates the mechanical connection of the intermediate shaft and uses a torque closed-loop algorithm to track the reference hand force, allowing for flexible design of driving feel styles. Compared to traditional EPS, which usually only has several styles such as comfort, standard, and sporty, SBW has more performance and can even be customized according to the driver's preferences.
Foldable steering wheel:
The adjustable range of the traditional EPS steering wheel is very limited, so even under automatic driving conditions such as APA/TJP/HWP, the steering wheel will continue to rotate. After the mechanical connection of the SBW is cancelled, the driver can choose to fold the steering wheel in an autonomous driving scenario, releasing more cockpit space for rest, entertainment, or work.
● Variable steering ratio:
The variable steering ratio function can balance flexibility under low vehicle speed conditions and stability under high vehicle speed conditions, or adjust the steering sensitivity of the steering wheel in the On Center and Off Center ranges. Due to the rigid mechanical connection of traditional EPS, achieving variable steering ratio requires changing the mechanical structure, such as gear rack transmission structure and steering column structure. The structure and control are complex and costly. For steering by wire (SBW), variable steering ratio can be achieved through software algorithms, which has great flexibility and can be flexibly defined within a safe range. The optimal driving experience can be achieved for different scenarios, such as racing mode, comfort mode, and operation mode.

Volkswagen I.D.Buzz concept car ThyssenKrupp foldable steering wheel (concept car)
Figure 3-3 Concept car with foldable steering wheel
● Automatic emergency steering:
Automatic Emergency Steering (AES) is a function that can effectively avoid vehicle collisions on open roads. Traditional EPS requires the steering wheel to quickly turn around an angle in a short period of time when the driver's hand is still in contact with the steering wheel, making it easy for the AES function to conflict with the driver's control and even cause panic. However, for the SBW system, when the automatic emergency steering function is activated, it can complete the emergency collision avoidance task in a short time without controlling the steering wheel, making it safer.
● Road interference suppression:
The Steering By Wire (SBW) system removes mechanical connections while also cutting off the path of noise transmission from the tires to the driver. Therefore, it can better suppress invalid interference signals on the road, reduce mechanical noise, make the cockpit quieter, and effectively improve the driving experience.
● Information and entertainment functions:
With the increasing intelligence of car cabins, the cockpit has become the second resting space for many consumers, with more and more information and entertainment functions. After removing the mechanical connection, the steering-by-wire system (SBW) can operate as a separate actuator, which can be used to link with the intelligent cockpit and serve as a game steering wheel. It also supports functions such as force feedback and vibration reminders.
4、 Summary
Compared to traditional EPS, Steer By Wire (SBW) technology has higher technical barriers, greater development difficulty, and higher development costs. However, SBW technology can support autonomous driving functions above L4 level, and can bring many new functions to cars, significantly improving the driving experience. Therefore, it is an inevitable trend in the development of automotive steering systems.
With the continuous development of wire controlled technology, the technology of wire controlled steering system (SBW) is becoming increasingly mature. Mainstream suppliers such as Bosch, ZF, Nexter, and Wandu have all completed the development of SBW products and are expected to complete mass production before 2025. Domestic component companies started relatively late compared to mainstream international suppliers, but are also rapidly catching up with national strategies. TrinovaSmart T-SBW solution makes cars smarter, safer, and more enjoyable to drive, helping customers create products that are more loved by consumers.
Recommended news
Online Message
Product Center
About Us
Beijing Office Address: Building 3, Yard 11, Rongxing North 1st Street, Beijing Economic and Technological Development Zone
Tianjin company address: Building 8, Robot Industry Accelerator, Automobile Industrial Park, Wuqing District, Tianjin
Service Hotline:022-59667907-8668
Company website:www.trinova-tech.com
E-mail: pr@trinova-tech.com
Follow Us

關注我們

Copyright◎Beijing Trinova Auto Tech Co.,Ltd 京ICP證000000号

